The Tasman Sea is a vast expanse of water located between Australia and New Zealand. It is named after the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman, who was the first European to explore the region in 1642. With an area of approximately 2.3 million square kilometers (890,000 square miles), the Tasman Sea is a critical component of the South Pacific Ocean and plays an essential role in the climate, economy, and culture of the region. The Tasman Sea is home to a diverse array of marine life, including dolphins, whales, seals, and various fish species, making it an important area for fishing, tourism, and scientific research.
Table of Contents
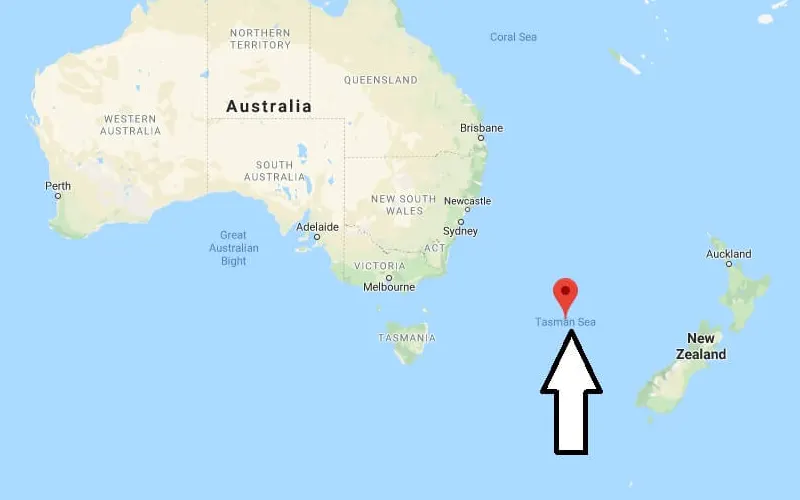
ToggleWhere Is Tasman Sea On The Map
The Tasman Sea is situated between the east coast of Australia and the west coast of New Zealand. It is bounded by Australia to the west, Tasmania to the south, and New Zealand to the east. The Tasman Sea is part of the South Pacific Ocean and is located south of the Coral Sea and north of the Southern Ocean.
On a map, the Tasman Sea can be seen as a large body of water in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, stretching over an area of approximately 2.3 million square kilometers. It is one of the most significant bodies of water in the region, and its location has played a critical role in the history, culture, and economy of both Australia and New Zealand.
Explorers Of Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea was first explored by the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman in 1642, who was searching for the fabled southern continent of Terra Australis. Tasman initially named the body of water “Zuydt Zee” (South Sea) but it was later renamed in his honor. Tasman made two voyages to the region, during which he also explored the coasts of present-day New Zealand and Australia.
Other notable explorers of the Tasman Sea include James Cook, who extensively charted the coastlines of Australia and New Zealand during his voyages in the late 18th century. Cook named many of the islands and bays in the region, and his detailed charts were used by subsequent explorers and navigators.
More recently, the Tasman Sea has been explored and studied by scientists and researchers from various disciplines, who have uncovered many new insights into the region’s geology, ecology, and oceanography.
Explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman was a Dutch explorer who played a significant role in the exploration of the Tasman Sea region. In 1642, Tasman set sail from Batavia (now Jakarta, Indonesia) with two ships, the Heemskerck and the Zeehaen, on a mission to explore the unknown regions to the south of the Dutch East Indies.
Over the course of his voyage, Tasman and his crew charted many new territories, including the western coast of Australia and the islands that now make up the nation of Vanuatu. However, it was his discovery of the island that would later be named Tasmania that would cement his place in history.
Tasman first sighted the island on November 24, 1642, and named it Anthoonij van Diemenslandt, after the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies. However, the name was later changed to Tasmania in honor of Tasman himself.
Tasman’s explorations in the Tasman Sea region opened up new possibilities for trade and colonization, and paved the way for further European exploration and settlement in the region. However, his voyages were also marked by conflict with the Indigenous peoples he encountered, and his legacy remains a subject of debate and discussion among historians and Indigenous communities alike.
Relationship Between The Tasman Sea And The Great Barrier Reef
The Tasman Sea and the Great Barrier Reef are geographically close to each other, but they are not directly connected. The Tasman Sea is located to the east of Australia and New Zealand, while the Great Barrier Reef is located in the Coral Sea off the northeast coast of Australia.
However, the Tasman Sea and the Coral Sea are both part of the larger South Pacific Ocean, and they share many similarities in terms of marine life and oceanographic conditions. Both regions are known for their rich biodiversity and support a wide range of marine species, including coral reefs, fish, turtles, and whales.
Additionally, the Tasman Sea and the Coral Sea have a shared history of exploration and exploitation by European navigators and colonizers, which has had a significant impact on the region’s Indigenous peoples and natural ecosystems.
What Is The Tasman Sea Known For?
The Tasman Sea is known for several distinctive features and characteristics that make it an important and unique part of the South Pacific Ocean. Here are some of the most notable things the Tasman Sea is known for:
- Challenging navigation: The Tasman Sea is a notoriously difficult body of water to navigate, with strong winds, rough seas, and limited sheltered areas.
- Marine biodiversity: The Tasman Sea is home to a diverse array of marine life, including dolphins, whales, seals, sharks, and numerous fish species.
- Economic importance: The Tasman Sea is a vital area for fishing, tourism, and scientific research, and plays an important role in the economies of Australia and New Zealand.
- Seismic activity: The Tasman Sea is located in a region with high levels of seismic activity, which can lead to earthquakes, tsunamis, and other natural disasters.
- Unique geological features: The Tasman Sea is home to a variety of unique geological features, including seamounts, deep sea trenches, and underwater mountains.
Overall, the Tasman Sea is an important and fascinating part of the world’s oceans, with a rich history and culture that continues to capture the imagination of people around the globe.
Where Does The Tasman Sea Start And End?
The Tasman Sea is a large body of water located between the eastern coast of Australia and the western coast of New Zealand. It stretches approximately 2,300 kilometers (1,400 miles) in length and 2,000 kilometers (1,200 miles) in width, and is part of the South Pacific Ocean.
The Tasman Sea is bounded by Australia to the west, Tasmania to the south, and New Zealand to the east. Its northern boundary is marked by a line drawn from Gabo Island, off the coast of Victoria in southeastern Australia, to Broughton Island, off the coast of New South Wales. Meanwhile, the southern boundary of the sea is defined by a line drawn from South Cape, the southernmost point of Tasmania, to the Southeast Cape, the southernmost point of New Zealand’s South Island.
The Tasman Sea is an important part of the region’s climate, economy, and culture. It is home to a diverse array of marine life, including dolphins, whales, seals, and various fish species. The sea is also a vital area for fishing, tourism, and scientific research.
Why Is Tasman Sea So Dangerous
The Tasman Sea is often regarded as a challenging and treacherous body of water, with a reputation for being dangerous for ships and boats to navigate. Several factors contribute to the perilous nature of the Tasman Sea:
- Strong winds: The region is prone to strong westerly winds that can produce high waves and rough seas, making it difficult for vessels to maintain their course and stability.
- Lack of shelter: The Tasman Sea has few natural harbors or sheltered areas, which means that ships must navigate open waters for extended periods without any protection from the elements.
- Remote location: The Tasman Sea is located far from major shipping lanes, which means that rescue and support can be slow to arrive in the event of an emergency.
- Cold water: The water in the Tasman Sea is generally cold, which can increase the risk of hypothermia for anyone who falls overboard.
- Seismic activity: The Tasman Sea is located in a region with high levels of seismic activity, which can lead to tsunamis, earthquakes, and other natural disasters that can endanger ships and boats.
These factors combine to make the Tasman Sea a challenging and dangerous environment for maritime navigation, and it requires careful planning, preparation, and skill to navigate safely.
Where Does Tasman Sea And Pacific Ocean Meet
The Tasman Sea and the Pacific Ocean meet along a line that extends from the southern tip of New Zealand’s South Island to the southeastern coast of Australia. This area is known as the “Tasman Fracture Zone,” and it marks the boundary between the two bodies of water.
The Tasman Fracture Zone is a region of deep water that is characterized by steep slopes and rugged terrain. The boundary between the Tasman Sea and the Pacific Ocean is not a distinct line, but rather a transitional zone where the waters of the two oceans mix and intermingle.
This boundary zone is home to a diverse array of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sharks, and various fish species. The area is also important for scientific research, as it provides valuable insights into the physical and biological processes that shape the ocean’s ecosystems and climate.
Why Tasman Sea Is Always Rough
The Tasman Sea is known for being a challenging body of water to navigate due to its strong winds, rough seas, and lack of sheltered areas. However, the conditions in the Tasman Sea can vary widely depending on the time of year, weather patterns, and other factors.
During the summer months, for example, the Tasman Sea tends to be calmer and more predictable, with milder winds and more moderate seas. However, during the winter months, the region is often hit by strong storms and heavy swells, which can create dangerous conditions for ships and boats.
In general, the Tasman Sea is characterized by a climate of changeability, with conditions that can shift rapidly and without warning. This makes it an unpredictable and challenging environment for sailors and other seafarers, and requires careful preparation and skill to navigate safely.
Marine Life And Biodiversity Of Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is home to a diverse range of marine life, from large mammals such as whales and dolphins to tiny planktonic organisms. Some of the most iconic species found in the Tasman Sea include humpback whales, southern right whales, orcas, bottlenose dolphins, and various species of seals and sea lions.
In addition to these large mammals, the Tasman Sea is also home to a wide variety of fish species, including several species of tuna, swordfish, and shark. Other notable fish species found in the Tasman Sea include barracuda, kingfish, and snapper.
The Tasman Sea is also home to a range of invertebrates, including various species of corals, sponges, and crabs. Some areas of the Tasman Sea are known for their extensive and diverse reef systems, which support a wide range of marine life.
Despite its rich biodiversity, the Tasman Sea is facing a range of threats, including overfishing, pollution, and climate change. Efforts are underway to protect and conserve the marine ecosystems of the Tasman Sea, but much more work is needed to ensure the continued survival of the diverse array of species that call it home.
Seismic Activity And Natural Disasters In The Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea region is known for its high levels of seismic activity, which are driven by the ongoing tectonic movements that are reshaping the landscape of the region. The Tasman Sea lies on the boundary between the Australian and Pacific tectonic plates, which are moving in opposite directions. This tectonic activity can result in earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other natural disasters.
One of the most significant earthquakes to occur in the Tasman Sea region was the magnitude 7.8 earthquake that struck the coast of New Zealand’s South Island in 2016. The quake triggered landslides, tsunamis, and other secondary hazards, causing widespread damage and several fatalities.
The Tasman Sea region has also experienced a number of tsunamis throughout history, including the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami, which was caused by a massive earthquake off the coast of Sumatra. The tsunami caused widespread devastation throughout the region, including in countries bordering the Tasman Sea.
Other natural disasters that have occurred in the Tasman Sea region include tropical cyclones, which can bring high winds and heavy rainfall to coastal communities, and bushfires, which are a recurring threat to many areas of Australia and New Zealand.
Despite the risks posed by seismic activity and natural disasters in the Tasman Sea region, efforts are underway to improve preparedness and response capabilities in order to minimize the impact of these events on local communities and the environment.
Conclusion
Despite its reputation as a dangerous place, the Tasman Sea is also a rich and diverse ecosystem, home to a wide variety of marine species and supporting a range of human activities, including fishing, shipping, and tourism.
The Tasman Sea is also steeped in history and culture, with a long tradition of Indigenous use and European exploration. Today, the Tasman Sea continues to be an important area of study for scientists, oceanographers, and policy-makers, as they work to understand and protect this vital part of the world’s oceans.