The Abyssal Zone is a deep, dark, and mysterious part of the ocean that is shrouded in mystery. This vast and remote region is located between 3,000 and 6,000 meters (9,800 to 19,700 feet) below the ocean’s surface, making it one of the most inhospitable places on Earth. Despite its inaccessibility, the Abyssal Zone is home to a diverse array of creatures, many of which are found nowhere else on the planet.
The purpose of this blog post is to explore the unique features of the Abyssal Zone and the fascinating creatures that call it home. We will delve into the depths of the ocean to discover what makes the Abyssal Zone such a special place, and we will learn about some of the creatures that have adapted to survive in this extreme environment.
Join us on this journey to the abyssal depths and discover the wonders that lie hidden beneath the waves.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is The Abyssal Zone?
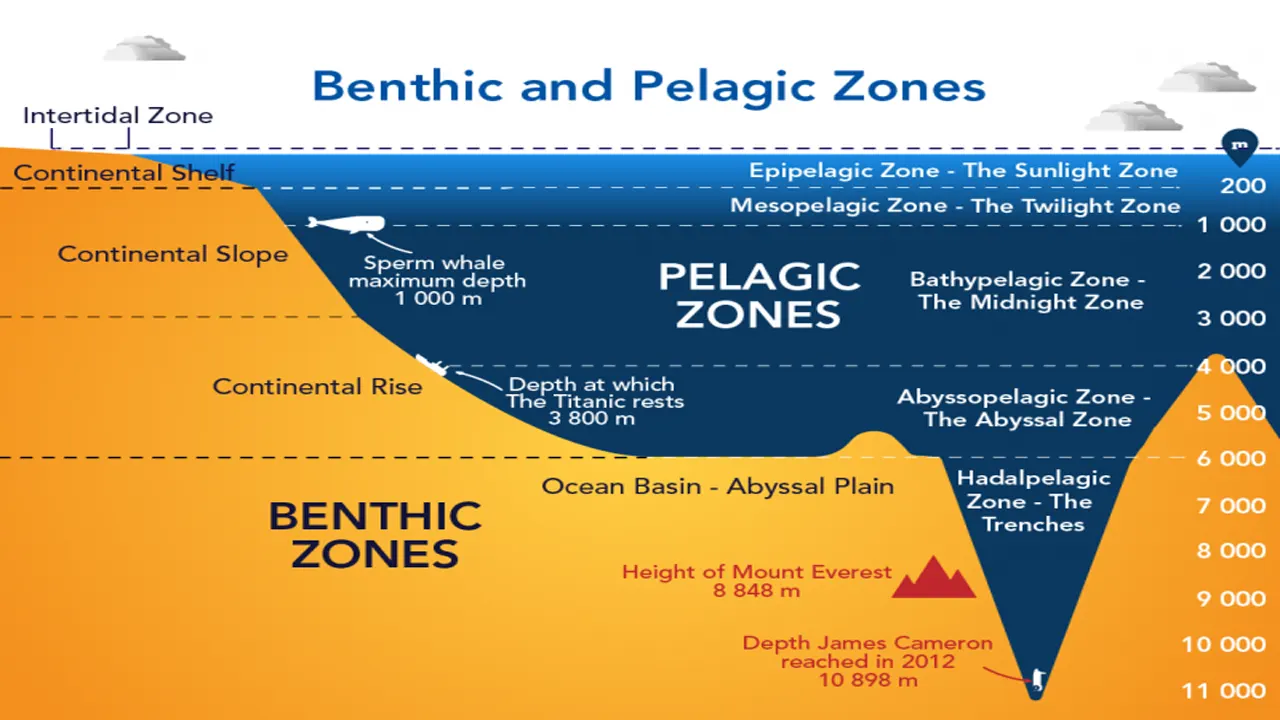
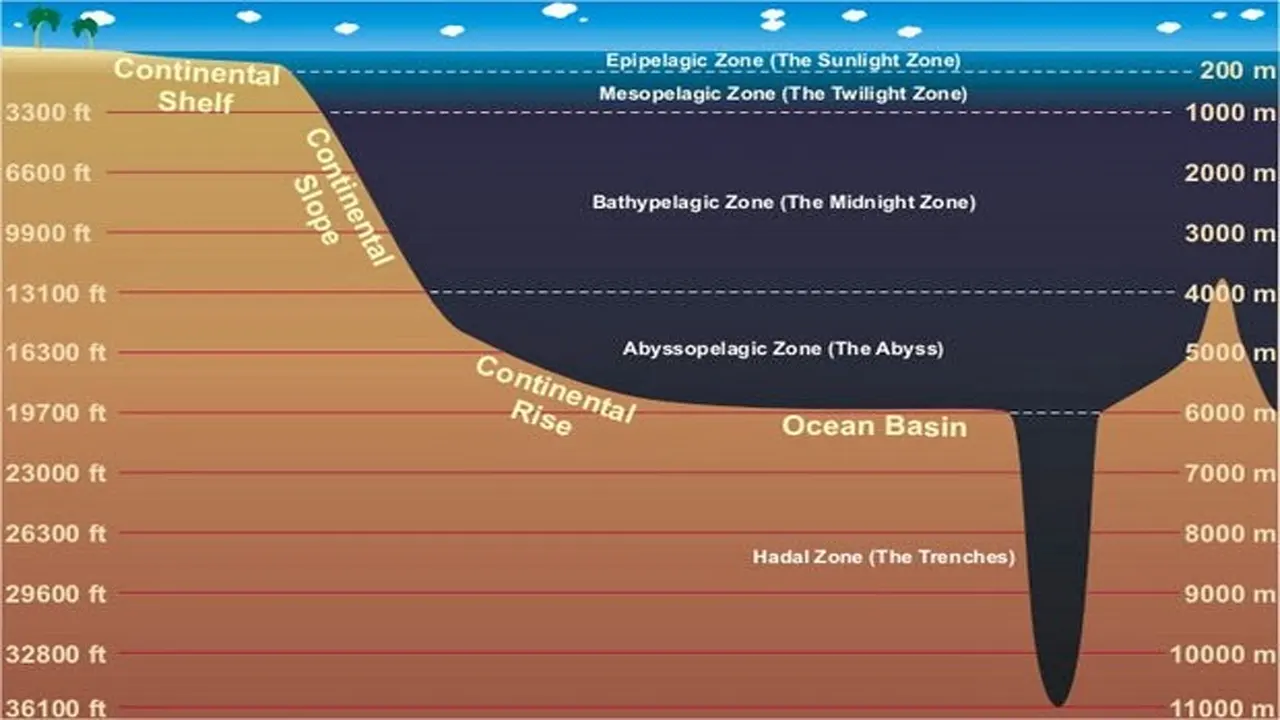
The Abyssal Zone is a vast region of the ocean that extends from about 3,000 to 6,000 meters (9,800 to 19,700 feet in length) below the surface. It is characterized by its complete darkness, cold temperatures, near freezing, and high water pressure. The temperature in the abyss ranges from just above freezing to a few degrees Celsius above that. Additionally, the pressure at these depths can reach up to 6,000 pounds per square inch (psi), which is more than 400 times the pressure at sea level.
The Abyssal Zone is so difficult to explore due to a number of technological and logistical challenges. First, the extreme depth and high pressure make it difficult for humans to travel to and work in the Abyssal Zone without specialized equipment.
Second, the darkness makes it challenging to navigate and observe the environment. Third, the logistics of deploying and retrieving equipment in such a remote and deep location can be complex and expensive. Finally, the extreme conditions of the Abyssal Zone can be damaging to equipment, making it difficult to collect data and samples.
Despite these challenges, advances in technology have allowed scientists to explore and study this mysterious region of the ocean more extensively in recent years.
Different Zones Of The Abyssal Zone
The abyssal zone is one of the most mysterious and fascinating regions of the ocean. This vast and deep area is often divided into different zones based on physical and biological factors. Some of the most notable zones of the abyssal zone include the sunlight zone, hadal zone, midnight zone, and twilight zone.
The sunlight zone, also known as the epipelagic zone, is the top layer of the ocean where sunlight can penetrate and support photosynthesis, and it is located above the abyssal zone. The hadal zone is the deepest part of the ocean. The depths of the hadal zone extends from approximately 6,000 to 11,000 meters (20,000 to 36,000 feet) below the surface. It is home to unique and extreme environments such as deep-sea trenches and canyons. The midnight zone, also known as the bathypelagic zone, extends from approximately 1,000 to 4,000 meters (3,300 to 13,100 feet) below the surface and is characterized by complete darkness. The twilight zone, also known as the mesopelagic zone, extends from approximately 200 to 1,000 meters (660 to 3,300 feet) below the surface and is where the last traces of sunlight can be detected.
Exploring the abyssal zone and its different zones requires specialized equipment and the expertise of marine biologists. These scientists study the deep ocean and its inhabitants to better understand the biology and ecology of this unique ecosystem. They use a variety of tools and techniques, such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), submersibles, and acoustic sensors, to explore the abyssal zone and its various zones.
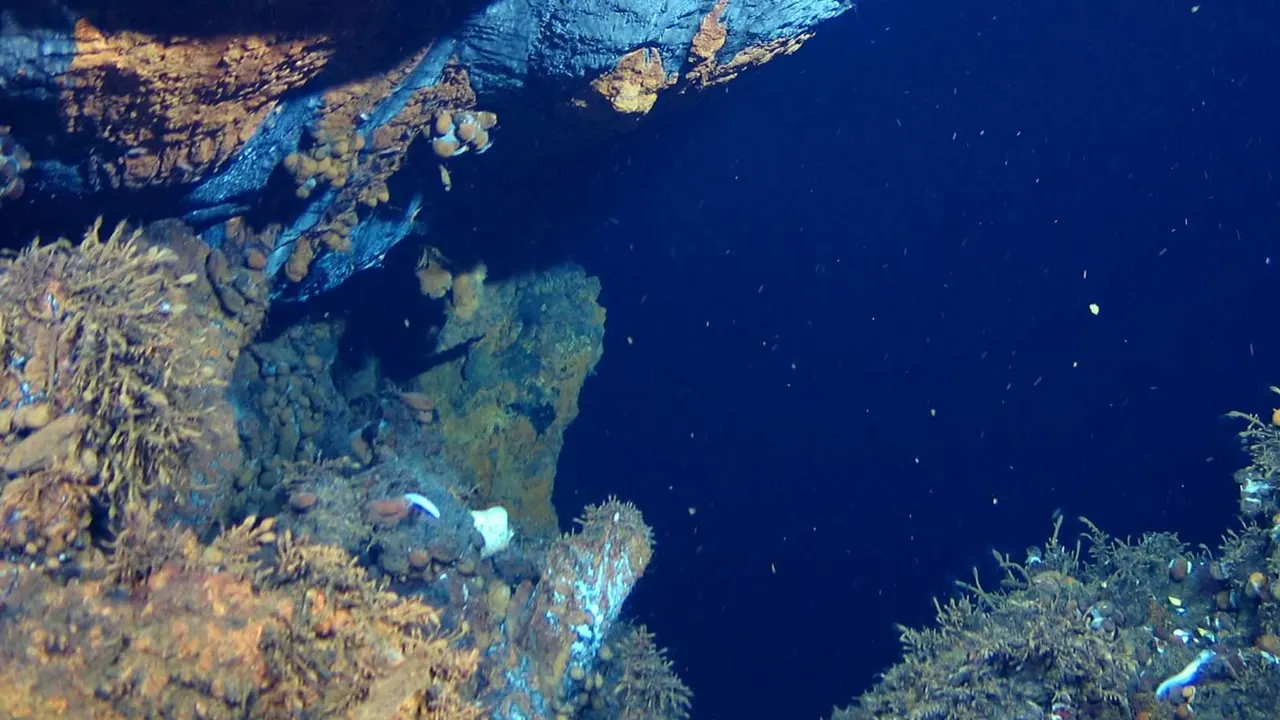
One of the most striking features of the abyssal zone is the sea floor, which is characterized by vast, flat areas known as abyssal plains. These plains are covered in a layer of sediment that provides habitat for a variety of organisms, including invertebrates, worms, and bacteria.
Floors Of The Abyssal Zone
The sea floor of the abyssal zone is a unique and fascinating habitat for a variety of organisms that live in the deep ocean. While the surface of the ocean is teeming with life, the abyssal zone is one of the least explored regions on Earth. Here are some interesting facts about the sea floor of the abyssal zone:
Marine snow: The sea floor of the abyssal zone receives a constant rain of organic material from the ocean surface, known as marine snow. This provides a source of food for many deep-sea organisms, including crustaceans and other scavengers.
Abyssal plains: The sea floor of the abyssal zone is often characterized by vast, flat areas known as abyssal plains. These plains are covered in a layer of sediment that can be several meters thick, providing a habitat for a variety of organisms.
Rugged terrain: While the abyssal plains make up a large portion of the sea floor in the abyssal zone, there are also areas of rugged terrain, such as seamounts and underwater mountains. These areas can provide important habitat for deep-sea organisms.
Deep-sea trenches: The abyssal zone also includes deep-sea trenches and canyons, which can be several kilometers deep. These areas are characterized by extreme pressure, low temperatures, and little to no sunlight.
Adaptations: Many of the organisms that live in the abyssal zone have adapted to the extreme conditions of this deep ocean habitat. For example, some crustaceans have evolved to live in the sediment at the bottom of the ocean, while others have developed bioluminescent abilities to communicate and find prey in the darkness.
Overall, the sea floor of the abyssal zone is a fascinating and important habitat for deep-sea organisms. While much of the ocean’s life is concentrated in shallower waters, the abyssal zone provides a unique opportunity for researchers to study the adaptations and ecology of organisms that thrive in this extreme environment.
Deep Sea Exploration
Ocean exploration has come a long way in recent years, with advances in technology and a growing understanding of the unique challenges posed by the deep sea environment. While the Abyssal Zone remains one of the most difficult areas to explore, new technologies like remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are making it increasingly possible to study this remote and largely unexplored environment.
For example, scientists have used ROVs and AUVs to explore hydrothermal vents, seamounts, and other unique features of the Abyssal Zone, capturing images and data that provide valuable insights into this ecosystem. These technologies have also allowed researchers to study the fascinating creatures that live in the deep sea, from bioluminescent fish to giant squid.
Looking to the future, there is no doubt that ocean exploration will continue to play an important role in advancing our understanding of the deep sea environment. With new technologies on the horizon, including advanced imaging techniques and even more advanced ROVs and AUVs, it is likely that we will continue to make new discoveries and gain new insights into the unique and mysterious world of the Abyssal Zone.
Unique Features Of The Abyssal Zone
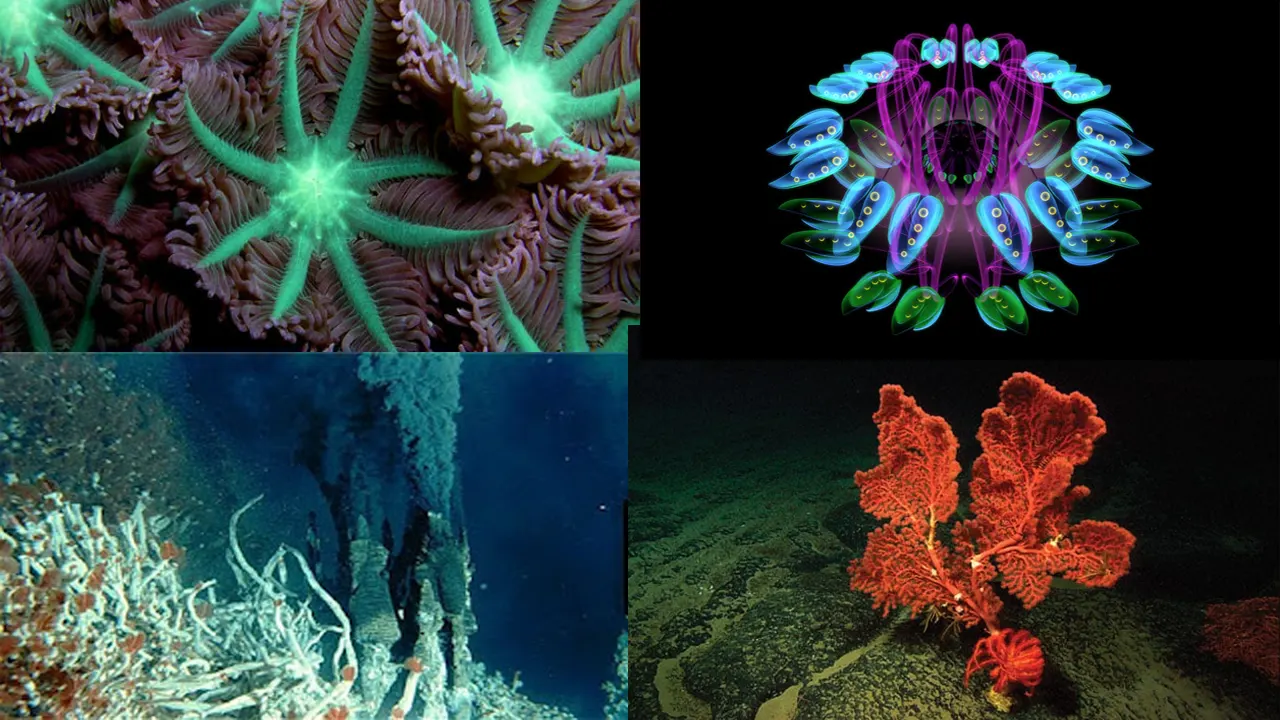
The Abyssal Zone is home to a number of unique features that make it a fascinating and diverse ecosystem. One of the most striking features are hydrothermal vents, which are cracks in the seafloor that release superheated water and minerals into the ocean. These vents can create unique habitats for creatures such as giant tube worms, shrimp, and crabs, which feed off the minerals and bacteria that thrive around the vents.
Another important feature of the Abyssal Zone are seamounts, which are underwater mountains that rise up from the seafloor. These seamounts can create habitats for a range of species, including deep-sea corals and fish. Some seamounts can also act as stepping stones for migrating species, allowing them to travel between different parts of the ocean.
The Abyssal Zone is also home to some of the deepest trenches in the ocean, such as the Mariana Trench. These deep trenches can create unique habitats for creatures that have adapted to survive at extreme depths and pressures, such as giant squid and certain types of amphipods.
The unique features of the Abyssal Zone create a complex and diverse ecosystem that supports a wide range of species. Despite the extreme conditions, many creatures have adapted to thrive in this challenging environment, creating a fascinating and mysterious abyssal world.
Creatures Of The Abyssal Zone
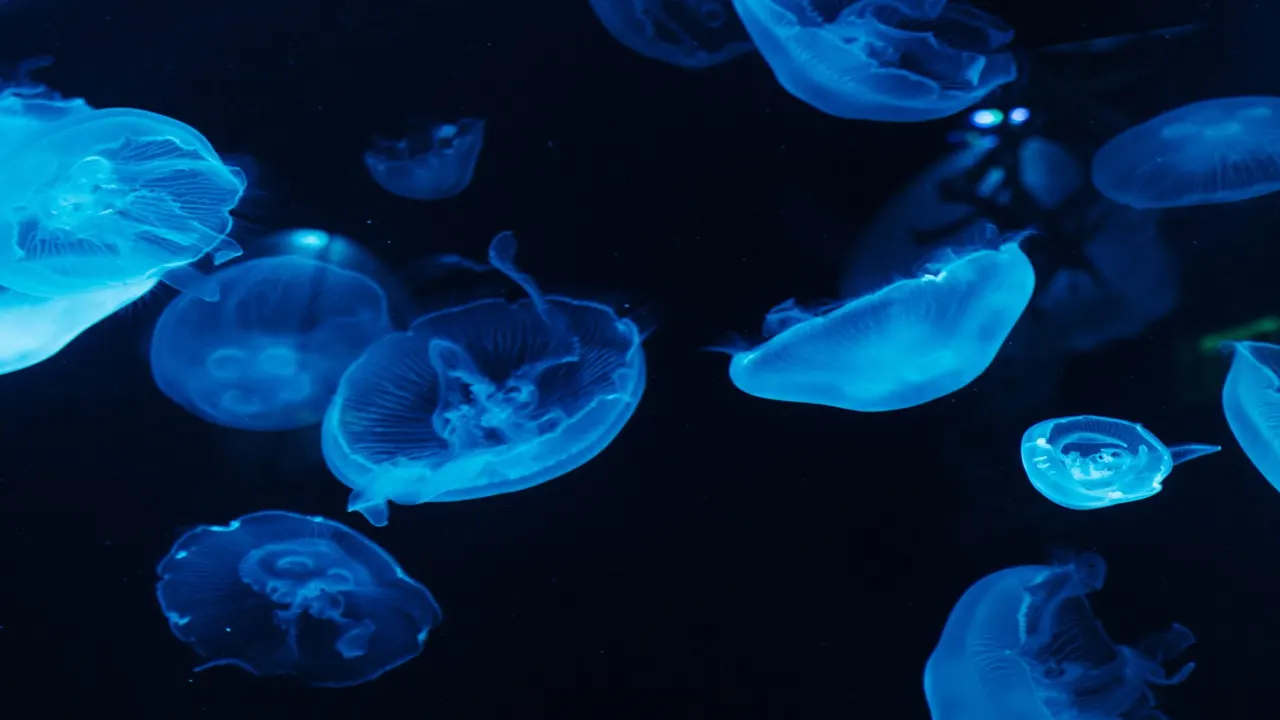
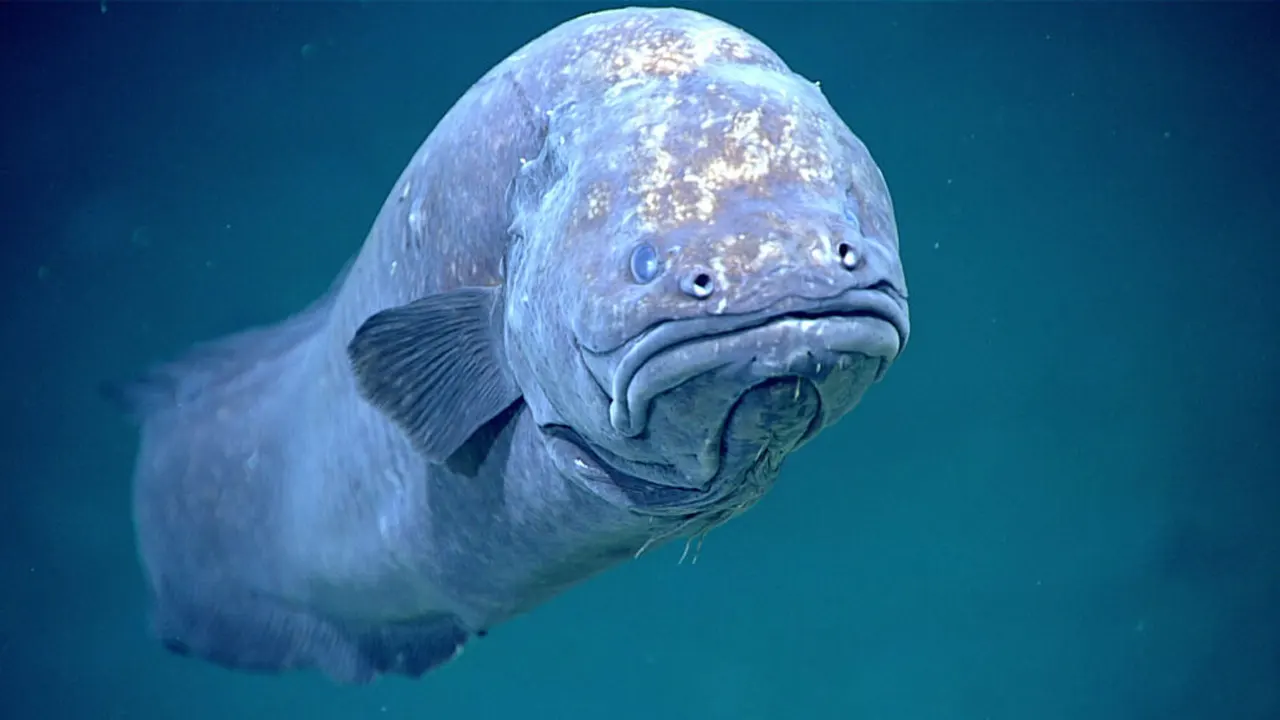
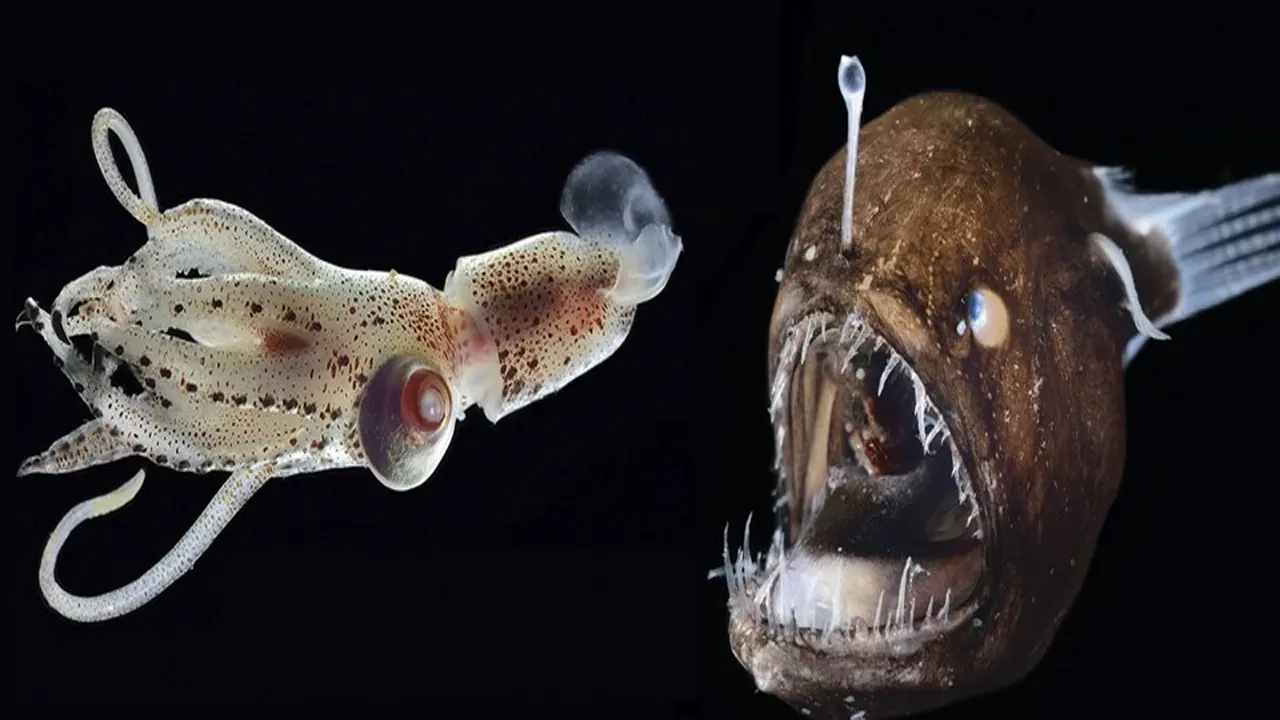
The Abyssal Zone is home to a wide variety of fascinating and unique creatures, many of which have evolved to survive in the extreme conditions of this deep and dark environment. One of the most famous creatures of the Abyssal Zone is the anglerfish, which uses a bioluminescent lure to attract prey in the darkness. Other notable species include the viperfish, which has large, sharp teeth and can grow up to two feet long, and the giant squid, which is one of the largest invertebrates in the world.
These creatures have adapted to the harsh conditions of the Abyssal Zone in a number of ways. For example, many have developed large eyes that are able to detect even the faintest traces of light in the darkness. Others have developed bioluminescent organs, which they use to communicate with other members of their species or to attract prey.
Another key adaptation among Abyssal Zone creatures is their ability to withstand extreme pressure. Some species have developed thick, gelatinous bodies that are able to withstand the crushing weight of the water at these depths. Others have evolved specialized air sacs that help them to regulate their buoyancy and stay afloat in the water column.
Overall, the creatures of the Abyssal Zone are an important part of the ecosystem in this unique and mysterious habitat. Their adaptations to the extreme conditions of this deep and dark environment are a testament to the incredible diversity and resilience of life on Earth.
Are There Plants In The Abyssal Zone?
The abyssal zone is a region of the ocean that is characterized by complete darkness, high pressure, and extreme cold temperatures. These environmental conditions make it difficult for photosynthetic organisms like plants to survive. Therefore, there are no plants or algae that grow in the abyssal zone.
Instead, the primary producers in the abyssal zone are chemosynthetic bacteria, which are capable of using chemical energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide, to produce organic matter. These bacteria form the base of the food chain in the deep ocean, providing a source of energy for other organisms such as tube worms, clams, and other invertebrates that are adapted to survive in this harsh environment.
What Happens When an Earthquake Strikes The Abyssal Zone?
There are several potential effects that could occur, such as:
Underwater landslides: The powerful forces of an earthquake can trigger landslides on the seafloor, which can cause debris to fall down into the abyssal zone and potentially damage or destroy the delicate ecosystems living there.
Tsunamis: Earthquakes can also generate massive waves known as tsunamis, which can travel across the ocean and affect the abyssal zone. These waves can displace water, cause currents to change, and lead to disruptions in the food chain.
Methane hydrate release: The shaking caused by earthquakes can sometimes trigger the release of methane hydrates from the seafloor, which are ice-like structures that contain methane gas. When these structures break apart, they can release large amounts of methane into the water, which can affect the chemistry of the ocean and contribute to climate change.
Overall, earthquakes can have significant impacts on the abyssal zone and the deep ocean ecosystem, and scientists are continuing to study the effects of seismic activity on this fragile environment.
Human Impact On The Abyssal Zone
Unfortunately, human activity is starting to have a significant impact on the Abyssal Zone and its unique ecosystem. One of the most pressing threats is deep-sea mining, which involves extracting minerals from the seafloor. This activity can cause significant damage to the fragile habitats around deep-sea vents and seamounts, which are home to a number of rare and unusual species.
Oil drilling is another major concern for the Abyssal Zone. Spills and leaks can have devastating impacts on the delicate balance of the ecosystem, potentially harming the many species that rely on the deep sea environment for survival.
Pollution is also a growing problem in the Abyssal Zone. Plastic waste and other debris from human activities can sink to the bottom of the ocean and accumulate in this deep and remote environment, where it can cause harm to the creatures that live there.
It is important to protect the Abyssal Zone and its unique inhabitants for a number of reasons. First, this deep and mysterious environment holds many secrets that have yet to be explored and understood. Scientists and biologists are still discovering new species and unlocking the secrets of bioluminescence and other adaptations that allow creatures to survive in this extreme environment.
Additionally, the Abyssal Zone plays an important role in the global oceanographic system, helping to regulate the circulation of water and nutrients around the world. By protecting this ecosystem, we can help to preserve the biodiversity of the ocean and ensure that this unique habitat continues to thrive for generations to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Abyssal Zone is a unique and mysterious part of our planet that is home to a wide variety of fascinating and unusual creatures. While the deep and dark environment of the Abyssal Zone poses significant challenges to exploration and study, advances in technology are making it increasingly possible for scientists and researchers to learn more about this remote and largely unexplored environment.
However, as human activity continues to impact the oceans, it is more important than ever to protect the Abyssal Zone and its unique inhabitants. By reducing pollution, regulating deep-sea mining and oil drilling, and taking other steps to protect the delicate balance of this ecosystem, we can help to ensure that the Abyssal Zone remains a vital and thriving part of the global oceanographic system for generations to come.